A new year is right around the corner and it is time to start thinking about how to improve your website and how your audience finds it. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a process you can apply in the creation of — or as ongoing maintenance to — your website. SEO affects your site’s online visibility in organic (unpaid) search results. To help you improve your website’s search optimization we put together these 8 Easy SEO Best Practices for 2018 that you can apply to your site today.
1. Clean Up Duplicates
On a regular basis, search engines like Google or Yahoo, run a “crawl” across websites. During these crawls, they analyze content and keywords to determine how a page should rank in search results on the internet. Of these crawlers, often known as “spiders” or “robots,” Googlebot is the most active bot and the most popular search engine. For those reasons, most SEO goals focus on improving results for Google. If not already familiar with search engine crawlers, you should check out Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Also, it never hurts to refresh yourself; the algorithm for site rankings changes often.
Many of these crawlers take looking for duplicates very seriously. To the robots, at least, duplicate content looks like you purposefully copied material to increase your ranking. To find out if you have any duplicate titles, meta descriptions, header tags, or URLs, run an SEO Audit on yourself. You can use tools like Screaming Frog (at cost) or Visual SEO Studio (free) to receive a report easily identifying these issues. Then, review and clean up those duplicates quickly so your site does not get penalized.
2. Consolidate Title and Meta Description Lengths
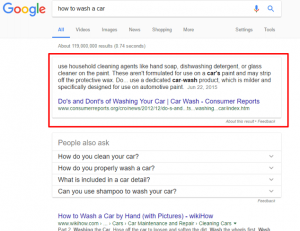
A simple rule to follow: keep your SEO Page Titles and Meta Descriptions at the length Google suggests. While a title can be up to 150 characters, Google recommends using only 70 (the amount of text that appears in the search engine results). Meta Descriptions can actually be as large as you want – but you should avoid that. Keep them below 160 characters, with your most critical information and keywords within that character count. Again, this matters because Google limits the displayed characters in its search engine results page (SERP) to 160 characters. You see an example of this in the following image:
There are always exceptions to the rule. For example, support centers tend to have very long, detailed questions submitted by customers. Sometimes, this creates long tail answers, as well. Do your best to consolidate those questions or answers, making it apparent that you have a great solution. However, these longer, more specific questions and answers can sometimes serve you. If the information pertains to a very niche market, and cannot be found on another site, longer questions and answers may appear higher in search rankings.
3. Write Concise Meta Descriptions
Now that you know the best practices for character quantities in a good meta description, we should talk about its quality. Within those 160 characters, you want to provide as much clear and useful information as possible. Your meta description sets forth what information your page contains, and will display as an excerpt or “snippet” in the search results to the user.
If you format your meta description clearly and concisely, Google will reward you by making that information the “featured snippet” at the top their results. They love lists, tables, graphs, and question-and-answer formats because it makes extracting relevant content easier. Proper tagging of key information like date of publication, author, and category will also help your site in search results.
However, Google will penalize you if you try to manipulate your content to play into this algorithm while creating a poor user experience. Getting to the top of the results is a great feat, but if your website visitors bounce shortly after their arrival, then you may have provided misleading information or a bad user experience. High click-through rates (CTR) from that landing page to other relevant pages on your site should top your list of primary goals. Once you get a visitor to your site, you want them to stay! Start considering a user’s experience above all else when creating or updating pages.
4. Stop Keyword Stuffing
Another reason search engines often penalize websites is for “keyword stuffing.” This occurs when a site overloads a webpage with keywords or phrases in an unnatural manner. While you should identify keywords for which you want your page to rank, Googlebot has become so sophisticated that it recognizes synonyms to relevant keywords. Write the way you would want to read information; do not worry about an exact keyword match. Also, do not cram your keyword(s) into your page in too abundant a manner, as in the following example:
As mentioned before, consider the user experience. Today, when people search for an answer or item online, they tend to search in a conversational manner. “How close is the nearest X?” is an example of that natural prose. This relates to the two ways in which we finding information today: by typing it out or through voice search. Digital assistants, like Siri or Alexa, have become more popular as we move closer to a hands-free device world. Optimize your page’s meta description or content around how you would normally ask or answer a question.
5. Hierarchy Over H1 Tags
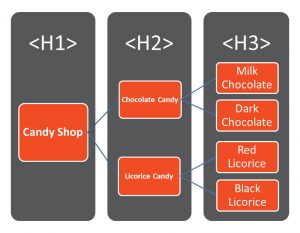
Heading tags help define sections of content on a web page as topics or subtopics. Google has always recommended that websites use keywords or phrases within their heading tags. They can range from H1 to H6, in order of most to least important. However, these days, site builders typically use tags more for styling purposes. Google has become savvy to this trend. As a result, Google now considers how you format and place your information in the hierarchy of a page or post more important than the exact keywords contained in heading tags.
Organize your content from most important to least important instead. Provide the answer your website visitor seeks toward the top of the page and as quickly as possible. Because crawlers consider the styling purposes of heading tags, you can place less emphasis on including the target keyword within (or as the first word of) the H1 tag. Just answer the question sooner rather than later, in that conversational tone, and you will move up in the rankings.
6. Quality Over Quantity
“More pages” and “quality content” do not mean the same thing. See how brief we kept that point? Stop pumping out more pages or posts on your website in hopes of attracting more attention. Filler content can actually bring your overall site ranking down because the content becomes either too niche or simply useless.
Consider revisiting old, popular articles or content from your site, then update them to continue to rank well. Make sure any new information provides something useful to your target audience and keeps them engaged during their visit. Just as important as the content you create, you should include quality links from one page to another. Do not load a page with irrelevant links to current content. Think about the user journey! Where would your users want to go next after reading or seeing that piece of content? More precisely, where do you want them to go next? Perhaps you seek to have them purchase a product, or share your content. Define those goals and it will pay off for you.
7. Images Matter, Too
While the information contained in a title, meta description, heading tag, and the content itself is extremely important, do not forget about an image’s alt text. Properly using alt text, you can both explain the subject matter of the image and cause it rank in search results for the words it contains.
Again, do not stuff the alt text with keywords, as search engines will penalize you. Instead, define the subject matter of the image as if describing it to a blind person. This includes context. Why does the image feature on this particular page? What makes it relevant to this specific content? Learn more about image publishing guidelines to start writing strong alt text.
8. Mobility Matters Most
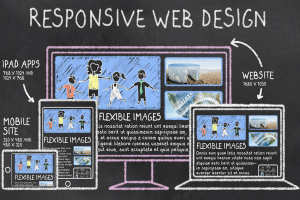
If your site lacks mobile-friendly formatting by 2018, Google will not like it. On April 21, 2015 Google updated their algorithm to prioritize sites that display well on mobile devices. This event came to be known as “Mobilegeddon.” At this point in time, you want your site to have responsive design. With a responsive design, your website detects the device used to view your site and its screen orientation, adjusting your site’s layout accordingly. Take Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to see if your site passes.
If you already have a mobile responsive design, start considering how your site’s elements display on these devices. Do you have a pop-up advertisement or module trying to capture data from a website visitor? If it gets in the way of a user accessing the content they clicked on from the search results, then you may have interrupted their visit, hampered engagement, and harmed your search ranking. Try using your site on several different types of devices to see what your users experience. Then, make changes that optimize that experience across all devices.
Final Thoughts
Search engines consider the user experience the most important factor in ranking pages in search results these days. As such, you should follow suit and make the user experience a top priority when considering any SEO changes.
Stop trying to beat the crawler’s algorithms, and start adapting your strategy around the user journey. These 8 SEO Best Practices for 2018 merely represent the starting point for improving your site’s rankings. So, start your site on the right path today.